FOR THREE YEARS, under presidents of both parties, the federal government has pumped trillions of borrowed dollars into stimulus, bailout, and recovery spending. The results have been woeful: Two years after the recession formally ended, the country is mired in a bleak economic lassitude from which it seems unable to rouse itself.
 With 14 million Americans still unemployed, President Obama is presiding over the weakest economic recovery in more than 60 years. |
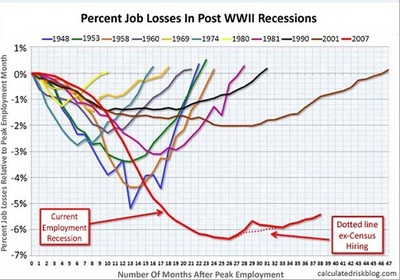
Now the wretched news of recent weeks -- feeble GDP growth; painful foreclosure rates; slipping car sales; a drop in factory orders; ever more Americans on food stamps -- has grown even worse.
First, Standard & Poor's reported that home prices have fallen to their lowest level in more than two years, confirming a "double dip" in a housing collapse more severe than the one during the Great Depression. Then came the government's latest employment numbers: only 54,000 jobs added in May, the fewest in eight months, and a rise in the unemployment rate to 9.1 percent. This has been the lousiest recovery in more than 60 years, and by a wide margin.
Last week, speaking at the Chrysler plant in Toldeo where the Jeep Wrangler is produced, President Obama tried to put a brave face on things. "There are always going to be bumps on the road to recovery," he said. "We're going to pass through some rough terrain that even a Wrangler would have a tough time with." The audience booed. If that's the reaction Obama's keep-your-chin-up rhetoric gets from a friendly union crowd, how will it play with the rest of the country?
In a new strategy memo, Democratic pollster Stan Greenberg warns his party that voters have lost confidence in Democrats when it comes to the economy, and that harping on the past -- insisting that "Democrats did right and brave things" to promote growth -- will not win votes in 2012.
"'The economy' is not the recovery," Greenberg writes, "but a set of powerful on-going realities: a middle class smashed and struggling, American jobs being lost, the country and people in debt. . . . Voters are desperate for leaders who understand the scope of what is happening. . . . They want serious plans, not triumphalism about jobs reports."
To Greenberg and other Democrats, "serious plans" to revive the economy presumably don't include dramatic cutbacks in the government's astronomical spending. But what if that spending -- projected to reach $3.8 trillion this year, $1.6 trillion of it borrowed -- is the very thing inhibiting economic growth? Keynesian economists and pundits have argued that what the economy craves is even more stimulus spending and government debt. But history suggests something altogether different.
Writing last year in the Cato Policy Report, economists Jason Taylor and Richard Vedder showed that the great post-World War II economic boom was ushered in by the swift rollback of what had been the largest economic "stimulus" in US history. At the time, leading Keynesians cautioned that the abrupt withdrawal of federal dollars would plunge the economy into a new depression.
Their warnings were ignored.
"Government canceled war contracts, and its spending fell from $84 billion in 1945 to under $30 billion in 1946," Taylor and Vedder wrote. "By 1947, the government was . . . running a budget surplus of close to 6 percent of GDP. The military released around 10 million Americans back into civilian life. Most economic controls were lifted, and all were gone less than a year after V-J Day. In short, the economy underwent . . . the 'shock of de-stimulus.'"
 Many economists warned that the federal government sharp spending cuts after World War II would trigger a new depression. Instead, the economy boomed. Above: Welch, West Virginia, 1946 |
Fearful predictions of massive unemployment -- 14 percent, Business Week said -- never materialized. Far from collapsing, "labor markets adjusted quickly and efficiently once they were finally unfettered." Even with millions of demobilized soldiers re-entering the workforce, "unemployment rates . . . remained under 4.5 percent in the first three postwar years." Workers who lost government-funded jobs quickly replaced them in the surging private sector. "In fact," Taylor and Vedder add, "civilian employment grew, on net, by over 4 million between 1945 and 1947 when so many pundits were predicting economic Armageddon. Household consumption, business investment, and net exports all boomed as government spending receded."
America's postwar experience indicates that vibrant growth is generated not by massive government interference in the economy, but by the reverse. The way to revive a gasping private sector is for government to get out of its way, not to choke it with trillions of dollars in new spending.
Washington's response to the recession -- unprecedented, intrusive, costly -- has been ruinous. The stimulus hasn't restored the economy to health. The "shock of de-stimulus" just might.
(Jeff Jacoby is a columnist for The Boston Globe).
-- ## --
Follow Jeff Jacoby on X (aka Twitter).
Discuss his columns on Facebook.
Want to read more? Sign up for "Arguable," Jeff Jacoby's free weekly email newsletter.

